If you’re learning about blockchain and cryptocurrency, you may have heard the word “node.” But what is a node in simple terms? Why are nodes important?
In this beginner-friendly article, we’ll explain what a node is, how it works, and why it plays a big role in keeping blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum running safely and smoothly.
Contents
What Is a Node?
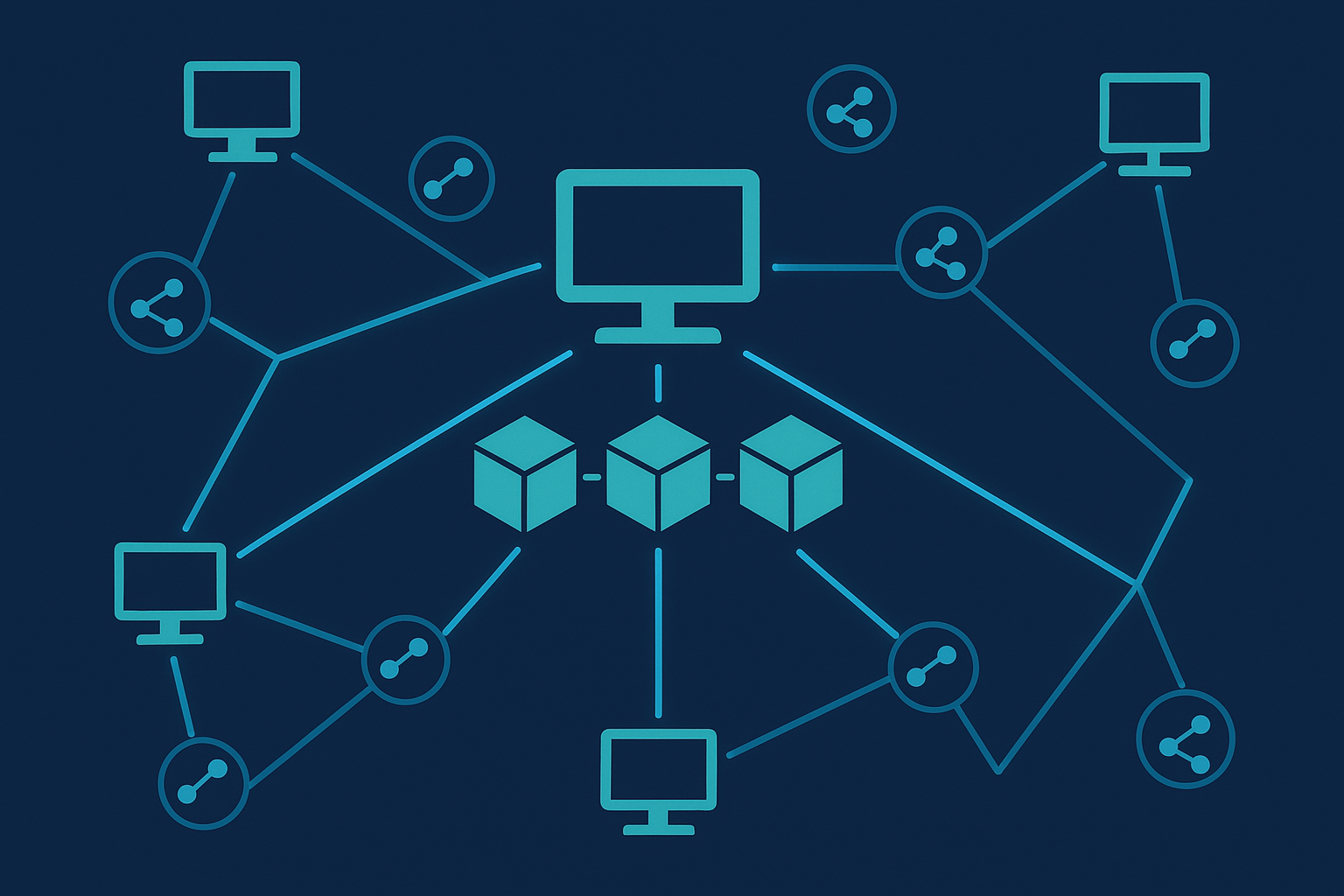
A node is a computer that connects to a blockchain network. Its job is to help run and maintain the blockchain.
Each node:
-
Shares information with other nodes
-
Helps confirm transactions
-
Stores a copy of the blockchain
In simple terms, a node is one of many computers that keep the blockchain alive and working.
Why Are Nodes Important?
Nodes make a blockchain decentralized. This means there is no single server or company in control. Instead, many nodes work together to manage the system.
The more nodes there are:
-
The more secure the network becomes
-
The harder it is for hackers to attack
-
The more reliable the blockchain is
If one node goes offline, the others keep everything running.
What Do Nodes Do?
Here are the main tasks that nodes perform:
✅ 1. Store the Blockchain
Many nodes keep a full copy of the entire blockchain history. This means they store every block and every transaction ever made.
These nodes are called full nodes.
✅ 2. Validate Transactions
Before a transaction is added to the blockchain, nodes check to make sure it’s valid.
Example: If Alice sends 1 BTC to Bob, the node checks if Alice actually has 1 BTC to send.
✅ 3. Help Add New Blocks
Some nodes help create new blocks and add them to the blockchain. This happens through:
-
Mining (in Proof of Work systems like Bitcoin)
-
Staking (in Proof of Stake systems like Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, Solana)
These nodes are called validator nodes or miner nodes.
✅ 4. Communicate Across the Network
Nodes talk to each other and share new transactions and block updates. This makes sure everyone sees the same data and stays in sync.
Types of Blockchain Nodes
There are different types of nodes, depending on their role:
| Node Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Node | Stores the entire blockchain and checks all transactions |
| Light Node | Stores only recent data, faster but less secure |
| Validator Node | Helps create new blocks by validating transactions (PoS) |
| Miner Node | Mines new blocks using computing power (PoW like Bitcoin) |
| Archive Node | Stores everything, including old data and states |
Most regular users connect with light nodes using wallets or apps, while developers and networks use full nodes.
Do You Need to Run a Node?
If you’re just buying, selling, or holding crypto, you don’t need to run your own node. Wallet apps like MetaMask or Trust Wallet connect to existing nodes for you.
But if you want to:
-
Help support the network
-
Have more control
-
Develop blockchain apps
…then running a node could be a great idea.
Is It Hard to Run a Node?
Running a node requires:
-
A computer with enough storage
-
A good internet connection
-
Some technical knowledge
It’s easier for some blockchains (like Solana or Cardano) and more demanding for others (like Ethereum full nodes).
There are also cloud-based services that make it easier to run a node without managing the hardware yourself.
Final Thoughts
A node is one of the key parts of a blockchain. It’s a computer that helps keep the network secure, updated, and running smoothly. Nodes work together to make sure everyone sees the same data and follows the same rules.
Without nodes, there would be no blockchain.
Even if you don’t run a node yourself, understanding how they work helps you see the power of decentralization and why blockchain is so trustworthy.