As more people use blockchain networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin, they sometimes become slow and expensive. This is where sidechains and Layer 2 solutions come in. These tools help blockchains work better by making transactions faster and cheaper.
In this beginner-friendly article, we’ll explain what sidechains and Layer 2 solutions are, how they work, and why they matter.
Contents
The Problem with Blockchains
Blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin are secure and decentralized, but they can be slow and costly, especially when lots of people are using them.
-
Transactions can take several minutes.
-
Fees (called gas fees) can be very high.
-
The network can become crowded.
To solve this, developers have created ways to move some of the work off the main blockchain. These solutions are called sidechains and Layer 2s.
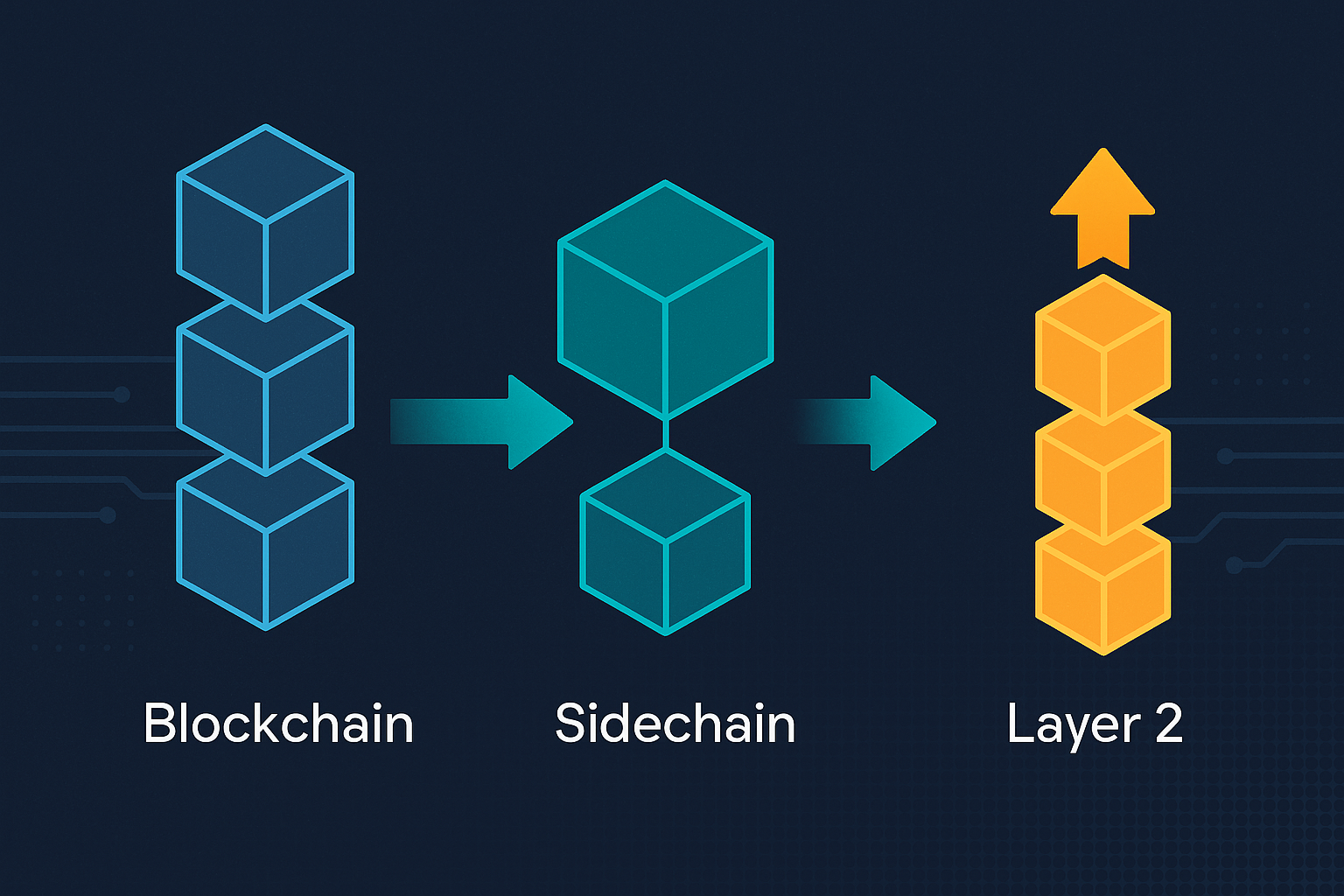
What Is a Sidechain?
A sidechain is a separate blockchain that is connected to a main blockchain (like Ethereum or Bitcoin). It works independently but can move data and tokens back and forth with the main chain.
Think of a sidechain like a side road next to a busy highway. Cars (transactions) can use the side road to avoid traffic, but they can also return to the highway when needed.
Features of Sidechains:
-
They have their own rules and validators.
-
They are usually faster and cheaper.
-
They communicate with the main blockchain using a special bridge.
Examples of Sidechains:
-
Polygon (PoS) – works with Ethereum
-
xDai Chain – used for fast and cheap payments
-
Rootstock (RSK) – works with Bitcoin
What Is a Layer 2 Solution?
A Layer 2 solution is built on top of an existing blockchain (called Layer 1). It doesn’t replace the main blockchain — it works with it to speed things up.
Layer 2s bundle many transactions together and then send a summary to the main blockchain. This reduces congestion and lowers fees.
Think of Layer 2 like a fast train running above a busy street. It carries people quickly but still connects to the same destination.
Features of Layer 2s:
-
Use the security of the main chain
-
Process transactions faster
-
Lower gas fees
-
Final results go back to Layer 1
Popular Layer 2 Solutions:
-
Arbitrum
-
Optimism
-
zkSync
-
Starknet
These are often used to speed up Ethereum.
Sidechain vs Layer 2: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Sidechain | Layer 2 Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Connection to Main Chain | Connected but independent | Built directly on top of Layer 1 |
| Security Source | Has its own security rules | Uses Layer 1 security |
| Speed and Cost | Fast and low fees | Also fast and low fees |
| Popular Examples | Polygon PoS, xDai, RSK | Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync |
Both improve blockchain performance — but in different ways.
Why Use Sidechains or Layer 2s?
-
Lower Fees: Pay less for sending or swapping tokens.
-
Faster Transactions: Get confirmations in seconds, not minutes.
-
Scalability: Handle more users at once without slowing down the network.
-
Better User Experience: Makes apps and games smoother for users.
If you’ve ever been frustrated by high Ethereum gas fees, these tools are for you.
How to Use Sidechains and Layer 2s
You can use these solutions easily with a wallet like MetaMask or Trust Wallet.
Example:
-
Bridge your tokens from Ethereum to a Layer 2 (like Arbitrum) or a sidechain (like Polygon).
-
Use apps (dApps) on that network to trade, swap, or play games.
-
Withdraw back to Ethereum if needed.
Just make sure to use official bridges and double-check network details before moving your funds.
Risks to Know
While sidechains and Layer 2s are helpful, there are some risks:
-
Bridge Risks: If a bridge is hacked, you may lose your funds.
-
New Technology: Some Layer 2s are still being tested.
-
Learning Curve: You need to learn how to switch networks and use bridges.
Start small and use trusted platforms to stay safe.
Final Thoughts
Sidechains and Layer 2 solutions are important tools that help blockchains grow and improve. They make crypto faster, cheaper, and easier to use.
Whether you’re trading tokens, using DeFi apps, or just exploring crypto, understanding these technologies can help you save time and money.