If you’re just starting to learn about blockchain, you may have heard the terms public blockchain and private blockchain. They sound similar, but they work very differently.
In this beginner-friendly article, we’ll explain what public and private blockchains are, how they work, and what makes them different. You don’t need any technical background — we’ll keep it simple and easy to understand.
Contents
What Is a Blockchain?
Before we talk about public and private blockchains, let’s quickly go over what a blockchain is.
A blockchain is a digital ledger. It stores data in “blocks” that are linked together. Each block contains information, and once it’s added, it cannot be changed easily. This makes blockchain a very secure and transparent way to store data.
Now, let’s dive into the two main types: public and private.
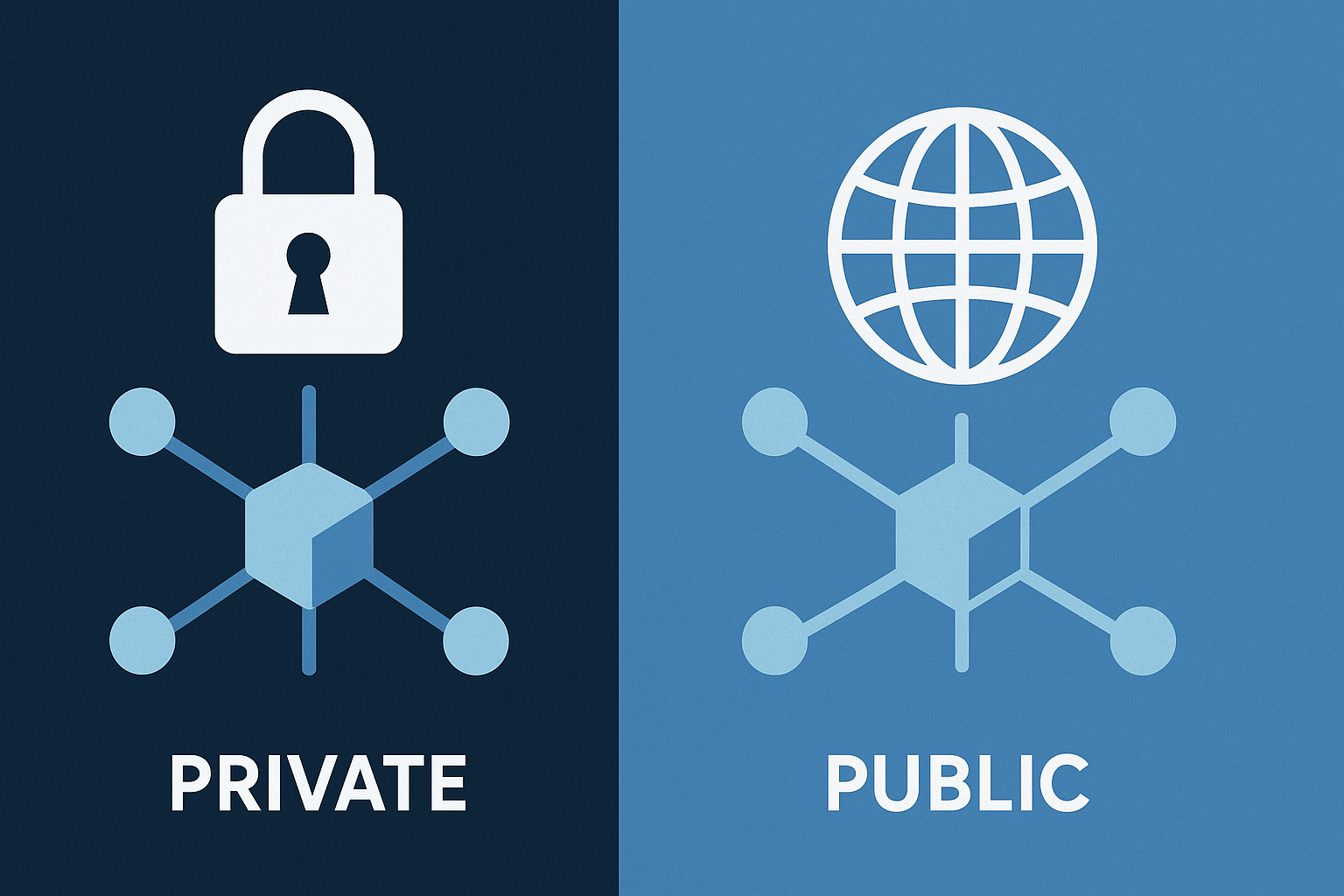
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain is open to everyone. Anyone in the world can:
-
Join the network
-
Read data
-
Make transactions
-
Help validate new blocks (this is called mining or staking)
These blockchains are fully decentralized, which means no single person or company controls them.
Examples of Public Blockchains:
-
Bitcoin
-
Ethereum
-
Litecoin
Key Features:
-
Open and transparent: Anyone can view the data.
-
Secure: Many users make it hard to hack.
-
Decentralized: No central authority.
Use Cases:
-
Cryptocurrency
-
Smart contracts
-
Decentralized apps (dApps)
What Is a Private Blockchain?
A private blockchain is not open to the public. Only selected people or organizations can:
-
Access the network
-
Read or write data
-
Validate transactions
Private blockchains are usually centralized — controlled by one company or group. They are often used by businesses for internal purposes.
Examples of Private Blockchains:
-
Hyperledger Fabric
-
Corda
-
Quorum
Key Features:
-
Access is restricted: Only invited members can join.
-
Faster transactions: Fewer users mean quicker processing.
-
More control: The company decides who can do what.
Use Cases:
-
Supply chain tracking
-
Banking and finance
-
Healthcare record management
Main Differences: Public vs Private Blockchain
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Open to everyone | Restricted to selected users |
| Control | Decentralized | Centralized |
| Speed | Slower (many users) | Faster (fewer users) |
| Transparency | Fully transparent | Limited visibility |
| Security | Very high | Still secure, but more trust-based |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum | Hyperledger, Corda |
Which One Is Better?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. It depends on your goals.
-
If you want open access and decentralization, a public blockchain is better.
-
If you need privacy, control, and speed, a private blockchain may be the right choice — especially for businesses.
Many companies are also exploring hybrid blockchains, which combine features of both public and private systems.
Why Should Beginners Care?
Understanding the difference between public and private blockchains helps you:
-
Choose the right projects to follow or invest in
-
Understand how companies use blockchain differently
-
Learn how decentralized and centralized systems work
Whether you’re into crypto trading or just curious about blockchain technology, knowing this difference is a great step forward.
Final Thoughts
To sum it up:
-
Public blockchains are open, secure, and decentralized — great for cryptocurrencies and open-source projects.
-
Private blockchains are closed, fast, and controlled — ideal for companies and private data.
Both have their place in the world of blockchain. Now that you understand how they differ, you’re better prepared to explore this exciting technology further.