Blockchain is the technology behind Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. It may sound complicated, but the basic idea is actually simple. In this article, you’ll learn how blockchain works, step by step, using easy language made for beginners.
Whether you’re new to crypto or just curious, this guide will help you understand the basics of blockchain technology.
Contents
What Is a Blockchain?
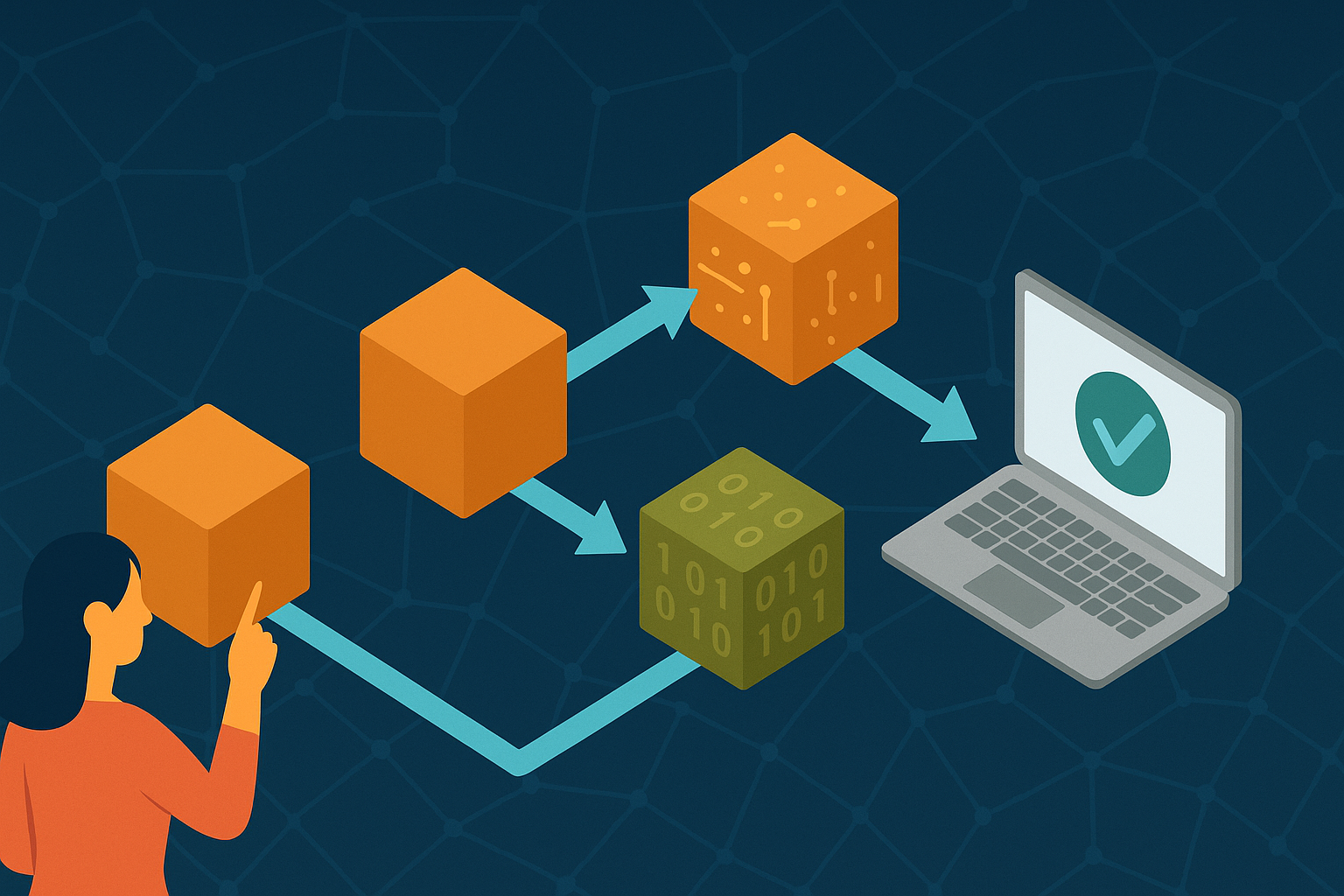
A blockchain is a type of database. But it’s different from a regular database. Instead of storing information in one place, a blockchain stores data in blocks that are linked together in a chain.
Once data is added to a block and added to the chain, it cannot be changed. That’s why blockchain is often called secure and tamper-proof.
Step-by-Step: How Blockchain Works
Let’s go through the process step-by-step to understand how a blockchain works.
Step 1: A Transaction Happens
Everything starts with a transaction. This can be someone sending Bitcoin to a friend, updating a digital contract, or recording ownership of a digital item.
Example:
Alice sends 0.5 BTC (Bitcoin) to Bob.
This transaction needs to be verified and added to the blockchain.
The transaction is sent to a network of computers called nodes. These nodes are spread all over the world. Each node has a copy of the blockchain.
All the nodes see that Alice wants to send Bitcoin to Bob.
Step 3: The Transaction Gets Verified
Before the transaction is added to the blockchain, the nodes need to agree that it’s valid. This process is called consensus.
In most blockchains like Bitcoin, this is done through a process called mining (or Proof of Work). Miners use computers to solve complex math problems. The first one to solve it gets to add a new block to the chain and earns a reward.
This process confirms that:
-
Alice has enough Bitcoin.
-
She hasn’t spent it twice.
-
The transaction is real.
Step 4: The Transaction Is Put into a Block
Once the transaction is verified, it is grouped with other transactions into a new block. A block can hold many transactions at once.
Each block also contains:
-
A timestamp
-
A reference to the previous block
-
A unique code called a hash
Step 5: The New Block Is Added to the Chain
After the block is created and verified, it is added to the blockchain. It is linked to the block before it, forming a chain of blocks — hence the name “blockchain.”
Now the transaction is complete and recorded forever.
Step 6: The Blockchain Is Updated Across the Network
Once the new block is added, all the nodes in the network update their copy of the blockchain. Everyone now sees that Alice sent Bitcoin to Bob.
This makes blockchain:
-
Decentralized (no single control)
-
Transparent (everyone can see the history)
-
Permanent (records cannot be changed)
Why Is Blockchain So Secure?
Blockchain is secure because:
-
Each block is linked to the previous one. If you try to change one block, the whole chain breaks.
-
Many computers must agree before anything is added.
-
Data can’t be changed after it’s added to the chain.
This is why blockchain technology is trusted for cryptocurrencies, digital contracts, supply chains, and more.
Real-Life Examples of Blockchain Use
-
Bitcoin & Ethereum – Cryptocurrencies that use blockchain to send money without banks.
-
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) – Digital art and items stored on blockchains.
-
Smart Contracts – Digital agreements that run automatically when conditions are met.
-
Supply Chain Tracking – Companies use blockchain to track goods from factory to store.
Final Thoughts
Now you know the basics of how blockchain works. It all starts with a transaction, which is verified, grouped into a block, and added to a chain that can’t be changed. It’s secure, transparent, and decentralized — perfect for a digital future.
Whether you want to invest in crypto or just understand the tech, learning blockchain is a smart first step.