If you’re new to crypto, you might have seen tokens like WBTC or WETH and wondered what they are. Why do they exist? Are they different from Bitcoin or Ethereum?
This article will explain what wrapped tokens are, why they’re useful, and how they help different cryptocurrencies work together — using simple and clear language for beginners.
Contents
What Is a Wrapped Token?
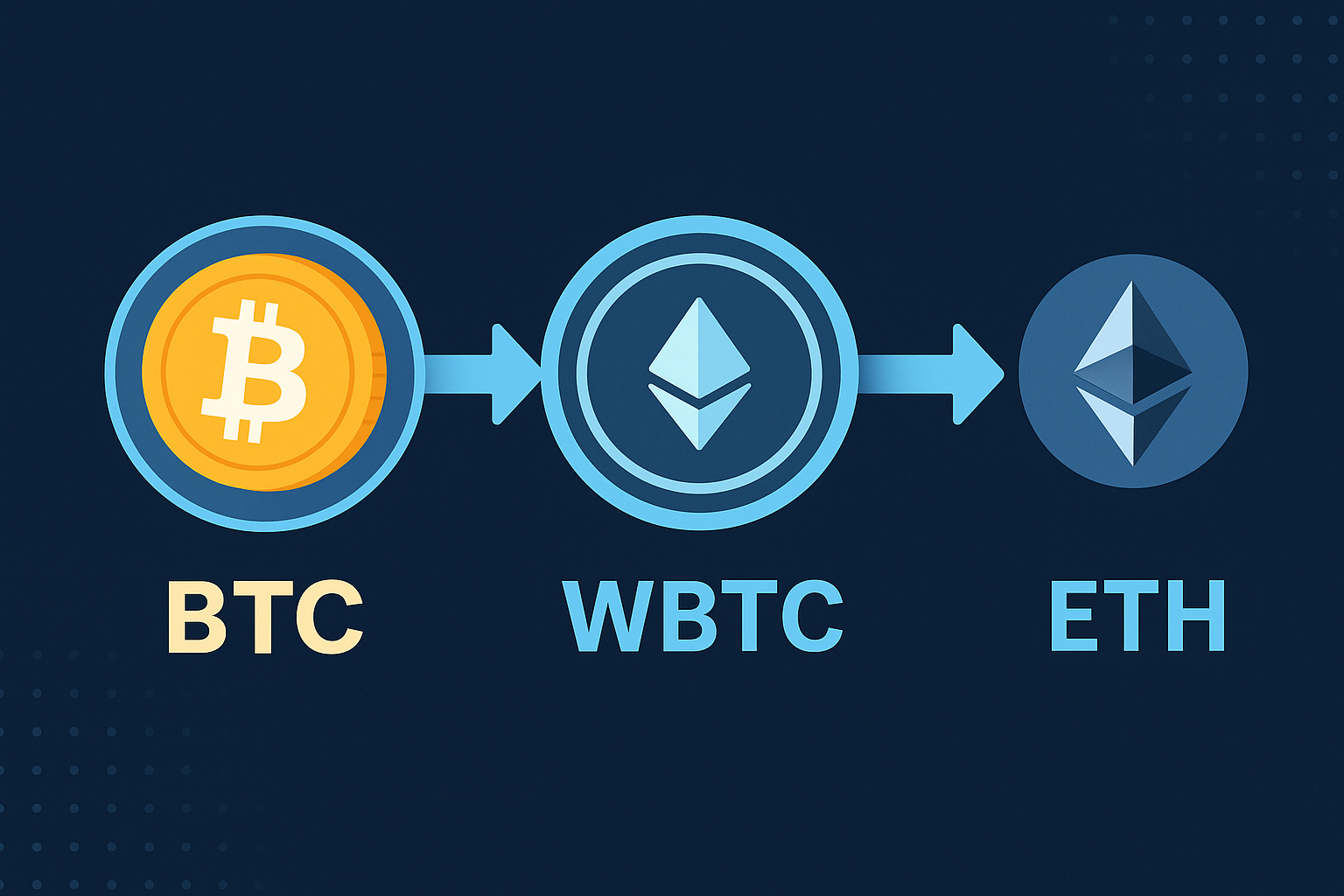
A wrapped token is a special version of a cryptocurrency that is made to work on another blockchain.
Here’s a simple way to understand it:
🔒 You take a real cryptocurrency (like Bitcoin)
🎁 Lock it up in a secure system (called a smart contract)
🔁 In return, you get a wrapped version of that crypto on another blockchain
So, Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is a version of Bitcoin that can be used on the Ethereum network.
Why Use Wrapped Tokens?
Most blockchains (like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana) are separate systems. They can’t easily talk to each other. Wrapped tokens solve this problem.
They allow people to:
✅ Use one cryptocurrency (like BTC) on another chain (like Ethereum)
✅ Trade more easily on decentralized apps (dApps)
✅ Join DeFi platforms that support only certain types of tokens (like ERC-20)
Wrapped tokens bring more flexibility and options to users without losing the value of the original asset.
What Is WBTC?
WBTC stands for Wrapped Bitcoin.
-
It is a 1:1 version of Bitcoin on the Ethereum network
-
1 WBTC = 1 BTC (always)
-
You can use WBTC in Ethereum dApps, like Uniswap or Aave
-
It follows the ERC-20 token standard, which is used by Ethereum apps
🔁 When you convert BTC to WBTC, your real Bitcoin is held by a custodian, and you get WBTC in return.
You can unwrap it anytime and get your BTC back.
What Is WETH?
WETH stands for Wrapped Ether.
Even though ETH (Ethereum’s native token) is already on the Ethereum network, it isn’t an ERC-20 token by default.
Many dApps use ERC-20 tokens, so WETH is used to wrap ETH and make it compatible with those systems.
-
1 WETH = 1 ETH
-
You can swap ETH to WETH inside many wallet apps (like MetaMask)
-
WETH is useful for DeFi, trading, and smart contracts
How to Get Wrapped Tokens
Getting wrapped tokens is simple:
To get WBTC:
-
Swap BTC for WBTC
-
Store WBTC in an Ethereum wallet like MetaMask
To get WETH:
-
Use a wallet or dApp like MetaMask or Uniswap
-
Swap your ETH for WETH
-
It stays in the same wallet — just a new format
You can also convert them back (unwrap) when you’re done.
Are Wrapped Tokens Safe?
Yes, but with some things to keep in mind:
✅ They are backed 1:1 with the original asset
✅ Big projects like WBTC use audited smart contracts
✅ Many are managed by trusted platforms and communities
However:
⚠️ You must use trusted services to wrap and unwrap
⚠️ Smart contract risks can still exist (bugs or hacks)
⚠️ Not all wrapped tokens are the same — check if they’re reliable and verified
Pros and Cons of Wrapped Tokens
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Use BTC on Ethereum | Requires trust in a custodian |
| More DeFi access and trading | Extra fees for wrapping/unwrapping |
| Improved blockchain compatibility | Smart contract risks |
| Greater liquidity for dApps | May confuse beginners |
Final Thoughts
Wrapped tokens like WBTC and WETH are powerful tools that make the crypto world more connected and usable. They help you do more with your crypto, without changing its value.
For beginners, the idea may sound confusing at first, but the main point is simple:
A wrapped token is the same value as the original, just in a different format that works on a specific blockchain.
Now that you understand wrapped tokens, you can explore more DeFi apps and tools with confidence.